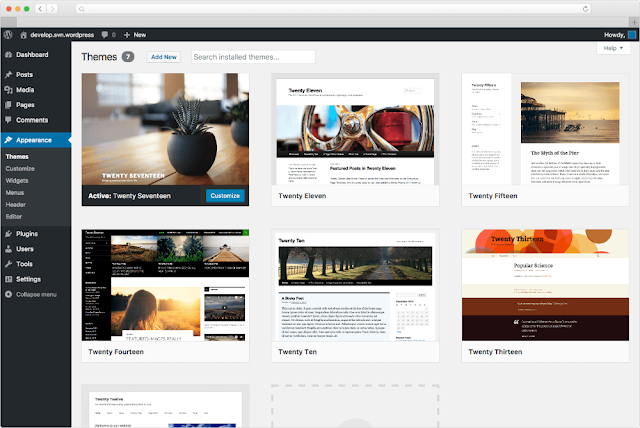
In WordPress, "Themes" refer to pre-designed templates that control the overall look and feel of your website. They determine the layout, color scheme, typography, and other design elements, allowing you to change the appearance of your website with just a few clicks. Themes play a crucial role in customizing the visual appearance of your WordPress site without the need for extensive coding.
Here's how themes work in WordPress:
Selecting a Theme: When you install WordPress, it comes with a default theme. However, you can change it to another theme that suits your website's purpose and style better. To do this, log in to your WordPress Dashboard, navigate to "Appearance" and click on "Themes." From there, you can browse a variety of free and premium themes available in the WordPress theme repository or upload a custom theme if you have one.
Installing and Activating Themes: Once you've found a theme you like, you can install it directly from the theme repository by clicking the "Install" button. After installation, click the "Activate" button to make the theme active on your website.
Customizing Themes: Many themes come with customization options that allow you to tailor the appearance to your liking. You can access the "Customize" option by clicking on "Customize" under the "Appearance" section. The customizer provides a live preview of your changes, allowing you to see how they affect your site before saving them.
Custom Page Templates: Some themes offer custom page templates, which are pre-designed layouts for specific types of pages (e.g., landing page, contact page). Using custom page templates, you can easily create pages with different designs and functionalities.
Child Themes: WordPress also supports child themes, which are themes that inherit the styles and functionality of a parent theme. Child themes are useful for making customizations to a theme while preserving the ability to update the parent theme without losing changes.
Responsive Design: Many modern themes are designed to be responsive, meaning they adapt and display well on various devices and screen sizes, such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Theme Updates: Themes are regularly updated to improve performance, fix bugs, and add new features. It's essential to keep your theme up to date to ensure compatibility and security.
Choosing the right theme is crucial as it sets the tone for your website and impacts user experience. Whether you're running a blog, e-commerce site, portfolio, or business website, there are themes available for every type of site. When selecting a theme, consider factors like responsiveness, customizability, support, and compatibility with plugins you plan to use.In WordPress, "Themes" refer to pre-designed templates that control the overall look and feel of your website. They determine the layout, color scheme, typography, and other design elements, allowing you to change the appearance of your website with just a few clicks. Themes play a crucial role in customizing the visual appearance of your WordPress site without the need for extensive coding.
Here's how themes work in WordPress:
Selecting a Theme: When you install WordPress, it comes with a default theme. However, you can change it to another theme that suits your website's purpose and style better. To do this, log in to your WordPress Dashboard, navigate to "Appearance" and click on "Themes." From there, you can browse a variety of free and premium themes available in the WordPress theme repository or upload a custom theme if you have one.
Installing and Activating Themes: Once you've found a theme you like, you can install it directly from the theme repository by clicking the "Install" button. After installation, click the "Activate" button to make the theme active on your website.
Customizing Themes: Many themes come with customization options that allow you to tailor the appearance to your liking. You can access the "Customize" option by clicking on "Customize" under the "Appearance" section. The customizer provides a live preview of your changes, allowing you to see how they affect your site before saving them.
Custom Page Templates: Some themes offer custom page templates, which are pre-designed layouts for specific types of pages (e.g., landing page, contact page). Using custom page templates, you can easily create pages with different designs and functionalities.
Child Themes: WordPress also supports child themes, which are themes that inherit the styles and functionality of a parent theme. Child themes are useful for making customizations to a theme while preserving the ability to update the parent theme without losing changes.
Responsive Design: Many modern themes are designed to be responsive, meaning they adapt and display well on various devices and screen sizes, such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Theme Updates: Themes are regularly updated to improve performance, fix bugs, and add new features. It's essential to keep your theme up to date to ensure compatibility and security.
Choosing the right theme is crucial as it sets the tone for your website and impacts user experience. Whether you're running a blog, e-commerce site, portfolio, or business website, there are themes available for every type of site. When selecting a theme, consider factors like responsiveness, customizability, support, and compatibility with plugins you plan to use.